The Measure
Restoring to a healthier estuary using more natural functional flows - including in-Delta flows and tributary input flows - to support ecological floodplain processes: Yolo Bypass floodplain inundation.
-
Expectations
More natural functional flow patterns are restored in the Yolo Bypass floodplain to support native fish spawning, and rearing along with important ecosystem processes.
-
Performance Metrics
- Area and duration of inundation in the Yolo Bypass, evaluated annually on a five-year rolling basis.
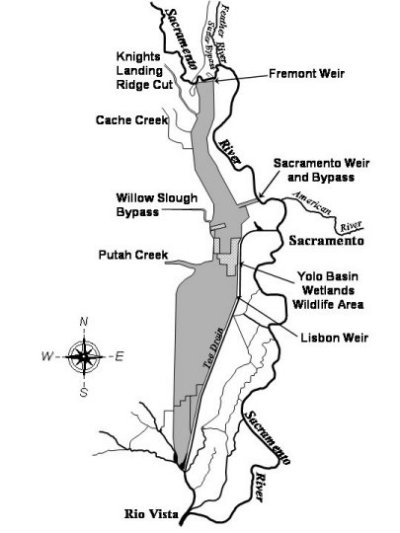
Yolo Bypass is a large floodplain habitat adjacent to the lower section of the Sacramento River that is frequently flooded and provides alternate routing of flows and young fish through the Delta. Floodplain inundation provides key ecological functions and restoring more natural functional flow patterns in the Yolo Bypass delivers important ecological benefits to fish in the lower Sacramento River.
The Yolo Bypass has been extensively studied for its potential to contribute to the growth of migratory fish species and contribution to the Delta food web. It has been consistently identified as a high opportunity area for providing floodplain and wetland functions. Native fish species such as Chinook salmon, steelhead, and Sacramento splittail accessing inundated habitat of the Yolo Bypass have higher growth rates and consequently increased survival rates. Juvenile fish migrating downstream through the Yolo Bypass also keep away from the southern Delta where mortality rates are higher. Food production (phytoplankton and zooplankton) and juvenile fish growth generally increase with increased floodplain inundation duration, although there is uncertainty as to the time period and frequency of inundation that provide maximum ecological benefits to the fisheries. Current collaborative and adaptive management efforts will provide additional information to guide the restoration of more natural flow patterns in the Yolo Bypass.
Yolo Bypass Salmonid Habitat Restoration and Fish Passage Project
DWR and U.S. Bureau of Reclamation developed the Yolo Bypass Salmonid Habitat Restoration and Fish Passage Project to improve fish passage and increase floodplain fisheries rearing habitat in Yolo Bypass and the lower Sacramento River basin. This mainly consist of a new Fremont Weir headworks structure, a new outlet channel, and downstream channel improvements. This project, known as the Big Notch Project, broke ground in June 2022 and is expected to be operational late 2024.
Each chapter of the Delta plan includes strategies to achieve the goals of the plan. These strategies are general guidance on achieving the objective laid out in the plan and in the Delta Reform Act of 2009. Associated with these strategies are recommendations. The recommendations describe more specific and implementable actions to support the achievement of Delta Plan strategies. Strategies and recommendations may also have associated performance measures. Delta Plan performance measures track progress in achieving desired outcomes for the Delta Plan. Below are the strategies and recommendations associated with this performance measure.
Delta Plan Strategy:
-
Create more natural functional flows
Delta Plan Recommendation:
- Update Delta flow objectives
Metric
Area and duration of inundation in the Yolo Bypass, evaluated annually on a five-year rolling basis.
Baseline
Modeling for the years 1997–2012 estimates that events with a 14-day duration inundated 45,100 acres in 33 percent of years, 19,700 acres in 50 percent of years, and 16,400 acres in 67 percent of years. Events with a duration of at least 21 days are estimated to have covered 36,300 acres in 33 percent of years, 15,800 acres in 50 percent of years, and 10,000 acres in 67 percent of years, between November 1 and May 30 (DWR 2015).
Target
By 2030, allow for at least 17,000 acres of inundation for at least 14 days in two out of three years and at least 21 days in one out of two years, between November 1 and March 15.
Flow data for at the Fremont Weir gage station (USGS) measuring daily flow into the Yolo Bypass
Water Year Summary for flow discharge data (USGS) at Fremont Weir
Flow data for at the Fremont Weir gage station (DWR) measuring daily flow into the Yolo Bypass
Recorded highest consecutive number of days with at least 6,000 cfs for each water year
Data from November 1 to March 15 of each water year were used
6,000 cfs was used as the target for Fremont Weir flows because it simulates inundation sufficient to support native wildlife species
